Expenses normally have debit balances that are increased with a debit entry. Since expenses are usually increasing, think “debit” when expenses are incurred. (We credit expenses only to reduce them, adjust them, or to close the expense accounts.) Examples of expense accounts include Salaries Expense, Wages Expense, Rent Expense, Supplies Expense, and Interest Expense. Each of the accounts in a trial balance extracted from the bookkeeping ledgers will either show a debit or a credit balance. The normal balance of any account is the balance (debit or credit) which you would expect the account have, and is governed by the accounting equation.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts: Methods of Accounting for – Investopedia
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts: Methods of Accounting for.
Posted: Tue, 29 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
From the table above it can be seen that assets, expenses, and dividends normally have a debit balance, whereas liabilities, capital, and revenue normally have a credit balance. As part of your review process, ensure that all trial balance accounts are posted to the general ledger. When you migrate to new accounting software systems, errors can occur without proper field mapping during the software conversion process. If the trial balance doesn’t balance, your accounting team should investigate and correct errors. During the accounting close process, check that the trial balance line items are included in the general ledger. After preparing your trial balance this month, you discover that it does not balance.
Trial Balance in Accounting: Definition, Types, & Examples
One way to find the error is to take the difference between the two totals and divide the difference by two. For this reason the account balance for items on the left hand side of the equation is normally a debit and the account balance for items on the right side of the equation is normally a credit. Accelerate your company’s accounting close by using automated batch payment reconciliation in Tipalti AP automation software. Read the white paper to learn more about holistic AP automation in accounting.

Because these have the opposite effect on the complementary accounts, ultimately the credits and debits equal one another and demonstrate that the accounts are balanced. Every transaction can be described using the debit/credit format, and books must be kept in balance so that every debit is matched with a corresponding credit. Third, the opposite holds true for liability, revenue, and equity accounts. The mnemonic for remembering this relationship is G.I.R.L.S. Accounts which cause an increase are Gains, Income, Revenues, Liabilities, and Stockholders’ equity.
What are the Limitations of a Trial Balance?
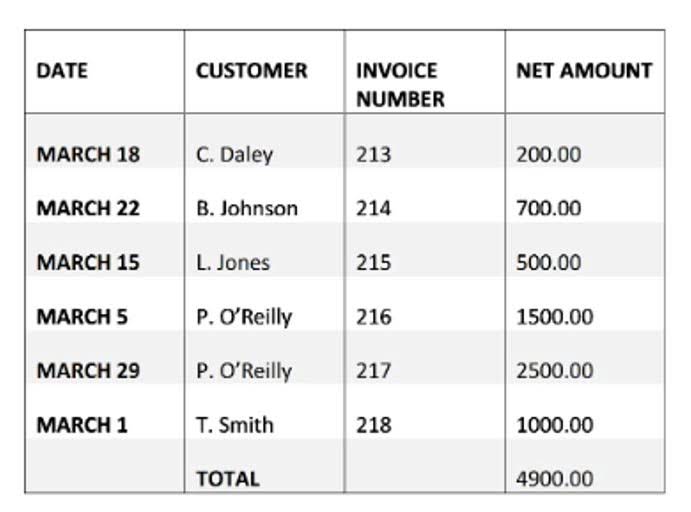
Since cash was paid out, the asset account Cash is credited and another account needs to be debited. Because the rent payment will be used up in the current period (the month of June) it is considered to be an expense, and Rent Expense is debited. If the payment was made on June 1 for a future month (for example, July) the debit would go to the asset account Prepaid Rent. For reference, the chart below sets out the type, side of the accounting equation (AE), and the normal balance of some typical accounts found within a small business bookkeeping system. Although companies also prepare a cash flow statement for cash flow management purposes and financial reporting, line items in the cash flow statement aren’t included in the trial balance. Let’s now take a look at the T-accounts and unadjusted trial balance for Printing Plus to see how the information is transferred from the T-accounts to the unadjusted trial balance.
- Bookkeepers and accountants or small business owners use different types of trial balance, depending on the stage of the accounting cycle close.
- If the final balance in the ledger account (T-account) is a debit balance, you will record the total in the left column of the trial balance.
- Accountants use trial balance reports and worksheets for a reporting period to determine whether the general ledger account debits and credits are in balance.
- Income statement accounts include Revenues, Cost of Goods Sold and Cost of Services, Expenses, gains, and losses.
- So for example there are contra expense accounts such as purchase returns, contra revenue accounts such as sales returns and contra asset accounts such as accumulated depreciation.
- Temporary accounts (or nominal accounts) include all of the revenue accounts, expense accounts, the owner’s drawing account, and the income summary account.
- Since the service was performed at the same time as the cash was received, the revenue account Service Revenues is credited, thus increasing its account balance.
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. Know which account should be coded as a debit and which account is a credit when recording transactions. Get enough training to handle relevant GAAP accounting principles correctly.
Contra Accounts
At the bottom of the trial balance report document, the Debit and Credit column totals are presented. According to the rules of double-entry accounting, total normal balance of accounts debits should equal total credits. Once all balances are transferred to the unadjusted trial balance, we will sum each of the debit and credit columns.
Another way to ensure that the books are balanced is to create a trial balance. This means listing all accounts in the ledger and balances of each debit and credit. Once the balances are calculated for both the debits and the credits, the two should match. If the figures are not the same, something has been missed or miscalculated and the books are not balanced. The typical type of balance for an asset on the balance sheet is a debit balance, whereas the typical balance for a liability account is a credit balance.
The unadjusted trial balance is the preliminary trial balance report or document that lists all ending balances or totals of accounts to determine if total debits and credit balances for account totals in the general ledger are equal. The trial balance is prepared after the subsidiary journals and journal entries have been posted to the general ledger. Double-entry bookkeeping requires that all accounting transactions have equal debits and credits. Accountants may use different types of trial balances for specific accounting tasks at different times.
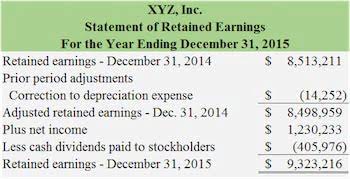
For example, asset accounts and expense accounts normally have debit balances. Revenues, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity accounts normally have credit balances. Accountants use trial balance reports and worksheets for a reporting period to determine whether the general ledger account debits and credits are in balance. Although using a trial balance can help detect accounting errors, some financial statement errors or omissions may not be prevented simply by using a trial balance.
